draw texture on 3d object
- Photoshop User Guide
- Introduction to Photoshop
- Dream information technology. Brand information technology.
- What'southward new in Photoshop
- Edit your first photo
- Create documents
- Photoshop | Common Questions
- Photoshop system requirements
- Migrate presets, actions, and settings
- Get to know Photoshop
- Photoshop and Adobe services
- Photoshop and Adobe Stock
- Creative Cloud Libraries
- Creative Cloud Libraries in Photoshop
- Use the Bear on Bar with Photoshop
- Work with Illustrator artwork in Photoshop
- Employ the Capture in-app extension in Photoshop
- Filigree and guides
- Creating actions
- Undo and history
- Default keyboard shortcuts
- Touch capabilities and customizable workspaces
- Photoshop on the iPad
- Photoshop on the iPad | Common questions
- Become to know the workspace
- System requirements | Photoshop on the iPad
- Create, open, and consign documents
- Add photos
- Work with layers
- Draw and paint with brushes
- Brand selections and add masks
- Retouch your composites
- Piece of work with aligning layers
- Adjust the tonality of your composite with Curves
- Apply transform operations
- Crop and rotate your composites
- Rotate, pan, zoom, and reset the canvas
- Work with Type layers
- Work with Photoshop and Lightroom
- Get missing fonts in Photoshop on the iPad
- Japanese Text in Photoshop on the iPad
- Manage app settings
- Impact shortcuts and gestures
- Keyboard shortcuts
- Edit your prototype size
- Livestream equally yous create in Photoshop on the iPad
- Correct imperfections with the Healing Brush
- Create brushes in Capture and utilize them in Photoshop
- Work with Camera Raw files
- Create and piece of work with Smart Objects
- Adjust exposure in your images with Contrivance and Burn
- Photoshop on the web beta
- Common questions | Photoshop on the spider web beta
- Introduction to the workspace
- Organization requirements | Photoshop on the web beta
- Keyboard shortcuts | Photoshop on the web beta
- Supported file types | Photoshop on the web beta
- Open and work with deject documents
- Collaborate with stakeholders
- Apply limited edits to your cloud documents
- Cloud documents
- Photoshop deject documents | Common questions
- Photoshop cloud documents | Workflow questions
- Manage and piece of work with deject documents in Photoshop
- Upgrade cloud storage for Photoshop
- Unable to create or save a cloud document
- Solve Photoshop deject document errors
- Collect cloud document sync logs
- Share access and edit your cloud documents
- Share files and comment in-app
- Workspace
- Workspace basics
- Create documents
- Use the Touch Bar with Photoshop
- Microsoft Dial support in Photoshop
- Tool galleries
- Operation preferences
- Utilize tools
- Touch gestures
- Impact capabilities and customizable workspaces
- Technology previews
- Metadata and notes
- Quickly share your creations
- Place Photoshop images in other applications
- Preferences
- Default keyboard shortcuts
- Rulers
- Show or hide not-printing Extras
- Specify columns for an prototype
- Undo and history
- Panels and menus
- Place files
- Position elements with snapping
- Position with the Ruler tool
- Presets
- Customize keyboard shortcuts
- Grid and guides
- Web, screen, and app design
- Photoshop for pattern
- Artboards
- Device Preview
- Re-create CSS from layers
- Slice spider web pages
- HTML options for slices
- Modify slice layout
- Work with web graphics
- Create web photo galleries
- Image and colour basics
- How to resize images
- Work with raster and vector images
- Epitome size and resolution
- Learn images from cameras and scanners
- Create, open, and import images
- View images
- Invalid JPEG Marking mistake | Opening images
- Viewing multiple images
- Customize colour pickers and swatches
- High dynamic range images
- Match colors in your image
- Catechumen betwixt colour modes
- Color modes
- Erase parts of an prototype
- Blending modes
- Choose colors
- Customize indexed color tables
- Image information
- Distort filters are unavailable
- About colour
- Color and monochrome adjustments using channels
- Cull colors in the Color and Swatches panels
- Sample
- Colour mode or Paradigm mode
- Colour cast
- Add a conditional manner change to an action
- Add swatches from HTML CSS and SVG
- Bit depth and preferences
- Layers
- Layer nuts
- Nondestructive editing
- Create and manage layers and groups
- Select, grouping, and link layers
- Identify images into frames
- Layer opacity and blending
- Mask layers
- Apply Smart Filters
- Layer comps
- Move, stack, and lock layers
- Mask layers with vector masks
- Manage layers and groups
- Layer effects and styles
- Edit layer masks
- Extract avails
- Reveal layers with clipping masks
- Generate image assets from layers
- Work with Smart Objects
- Blending modes
- Combine multiple images into a group portrait
- Combine images with Motorcar-Blend Layers
- Align and distribute layers
- Copy CSS from layers
- Load selections from a layer or layer mask's boundaries
- Knockout to reveal content from other layers
- Layer
- Flattening
- Composite
- Background
- Selections
- Select and Mask workspace
- Make quick selections
- Get started with selections
- Select with the marquee tools
- Select with the lasso tools
- Select a color range in an image
- Adjust pixel selections
- Convert between paths and selection borders
- Channel basics
- Motion, copy, and delete selected pixels
- Create a temporary quick mask
- Save selections and alpha aqueduct masks
- Select the image areas in focus
- Duplicate, split, and merge channels
- Channel calculations
- Selection
- Bounding box
- Epitome adjustments
- Perspective warp
- Reduce camera shake blurring
- Healing brush examples
- Export colour lookup tables
- Adjust image sharpness and blur
- Understand color adjustments
- Utilize a Brightness/Contrast adjustment
- Adjust shadow and highlight item
- Levels aligning
- Conform hue and saturation
- Accommodate vibrance
- Conform color saturation in epitome areas
- Make quick tonal adjustments
- Apply special color effects to images
- Raise your image with colour balance adjustments
- High dynamic range images
- View histograms and pixel values
- Match colors in your image
- How to crop and straighten photos
- Catechumen a color paradigm to blackness and white
- Adjustment and fill layers
- Curves adjustment
- Blending modes
- Target images for printing
- Adjust color and tone with Levels and Curves eyedroppers
- Adjust HDR exposure and toning
- Filter
- Blur
- Dodge or burn down paradigm areas
- Make selective colour adjustments
- Replace object colors
- Adobe Camera Raw
- Camera Raw system requirements
- What's new in Photographic camera Raw
- Introduction to Camera Raw
- Create panoramas
- Supported lenses
- Vignette, grain, and dehaze effects in Camera Raw
- Default keyboard shortcuts
- Automatic perspective correction in Camera Raw
- How to make not-destructive edits in Photographic camera Raw
- Radial Filter in Camera Raw
- Manage Camera Raw settings
- Open, process, and save images in Camera Raw
- Repair images with the Enhanced Spot Removal tool in Camera Raw
- Rotate, crop, and adjust images
- Adjust color rendering in Camera Raw
- Feature summary | Adobe Camera Raw | 2022 releases
- New features summary
- Procedure versions in Camera Raw
- Make local adjustments in Camera Raw
- Prototype repair and restoration
- Remove objects from your photos with Content-Aware Fill
- Content-Enlightened Patch and Movement
- Retouch and repair photos
- Correct paradigm distortion and noise
- Bones troubleshooting steps to gear up most issues
- Image transformations
- Transform objects
- Arrange crop, rotation, and canvas size
- How to crop and straighten photos
- Create and edit panoramic images
- Warp images, shapes, and paths
- Vanishing Indicate
- Use the Liquify filter
- Content-enlightened scaling
- Transform images, shapes, and paths
- Warp
- Transform
- Panorama
- Drawing and painting
- Pigment symmetrical patterns
- Draw rectangles and modify stroke options
- Nigh cartoon
- Draw and edit shapes
- Painting tools
- Create and modify brushes
- Blending modes
- Add together color to paths
- Edit paths
- Paint with the Mixer Castor
- Brush presets
- Gradients
- Gradient interpolation
- Fill and stroke selections, layers, and paths
- Draw with the Pen tools
- Create patterns
- Generate a pattern using the Pattern Maker
- Manage paths
- Manage pattern libraries and presets
- Draw or pigment with a graphics tablet
- Create textured brushes
- Add dynamic elements to brushes
- Gradient
- Paint stylized strokes with the Art History Brush
- Paint with a design
- Sync presets on multiple devices
- Text
- Piece of work with OpenType SVG fonts
- Format characters
- Format paragraphs
- How to create blazon furnishings
- Edit text
- Line and character spacing
- Arabic and Hebrew type
- Fonts
- Troubleshoot fonts
- Asian blazon
- Create blazon
- Text Engine error using Type tool in Photoshop | Windows viii
- Globe-Ready composer for Asian Scripts
- How to add and edit the text in Photoshop
- Video and blitheness
- Video editing in Photoshop
- Edit video and animation layers
- Video and animation overview
- Preview video and animations
- Pigment frames in video layers
- Import video files and paradigm sequences
- Create frame animations
- Creative Cloud 3D Blitheness (Preview)
- Create timeline animations
- Create images for video
- Filters and effects
- Use the Liquify filter
- Utilize the Blur Gallery
- Filter nuts
- Filter furnishings reference
- Add together Lighting Effects
- Utilise the Adaptive Wide Angle filter
- Use the Oil Paint filter
- Layer effects and styles
- Apply specific filters
- Smudge image areas
- Saving and exporting
- Salvage your files in Photoshop
- Export your files in Photoshop
- Supported file formats
- Relieve files in graphics formats
- Move designs between Photoshop and Illustrator
- Relieve and consign video and animations
- Save PDF files
- Digimarc copyright protection
- Salvage your files in Photoshop
- Printing
- Print 3D objects
- Print from Photoshop
- Print with color direction
- Contact Sheets and PDF Presentations
- Print photos in a picture package layout
- Print spot colors
- Duotones
- Print images to a commercial press press
- Meliorate color prints from Photoshop
- Troubleshoot printing issues | Photoshop
- Automation
- Creating actions
- Create information-driven graphics
- Scripting
- Process a batch of files
- Play and manage actions
- Add provisional actions
- About actions and the Actions console
- Record tools in actions
- Add a conditional mode change to an activity
- Photoshop UI toolkit for plug-ins and scripts
- Colour Management
- Understanding color direction
- Keeping colors consistent
- Colour settings
- Work with color profiles
- Colour-managing documents for online viewing
- Color-managing documents when printing
- Colour-managing imported images
- Proofing colors
- Content authenticity
- Learn about content credentials
- Identity and provenance for NFTs
- Connect accounts for artistic attribution
- 3D and technical imaging
- Photoshop 3D | Common questions around discontinued 3D features
- Creative Cloud 3D Blitheness (Preview)
- Print 3D objects
- 3D painting
- 3D console enhancements | Photoshop
- Essential 3D concepts and tools
- 3D rendering and saving
- Create 3D objects and animations
- Epitome stacks
- 3D workflow
- Measurement
- DICOM files
- Photoshop and MATLAB
- Count objects in an image
- Combine and convert 3D objects
- 3D texture editing
- Adjust HDR exposure and toning
- 3D panel settings
You can use any Photoshop painting tools to paint direct on a 3D model just equally you would on a 2D layer. Use choice tools to target specific model areas or allow Photoshop identify and highlight paintable areas. 3D menu commands permit you clear away areas of a model to access interior or subconscious portions for painting.
When painting directly on the model, you can choose which underlying texture map to apply paint to. Typically pigment is applied to the diffuse texture map, which gives a model material its color properties. Yous tin can also paint on other texture maps, such equally the bump map or opacity map. If y'all pigment on an expanse of the model that lacks the blazon of texture map y'all're painting on, a texture map is automatically created.
Bachelor 3D painting methods
Different painting methods are appropriate for different utilise cases. Photoshop provides the following 3D painting methods:
Live 3D Painting: (Default in Photoshop) Brush strokes made in the 3D model view or the texture view are reflected in existent time in the other view. This 3D painting method offers high functioning and minimum distortion.
Layer Projection Painting: The Gradient tool and filters use this painting method. The Layer Projection Painting method involves merging a painted layer with the underlying 3D layer. During the merge performance, Photoshop automatically projects the paint onto the appropriate target textures.
Projection Painting: (Default in Photoshop Extended CS6) Projection Painting is suitable for painting multiple textures simultaneously or for painting the seam between ii textures. All the same, in full general, it is a lower-functioning painting method and may result in cracks when you're painting complex 3D objects.
Texture Painting: You can open the 2D texture and paint it directly.
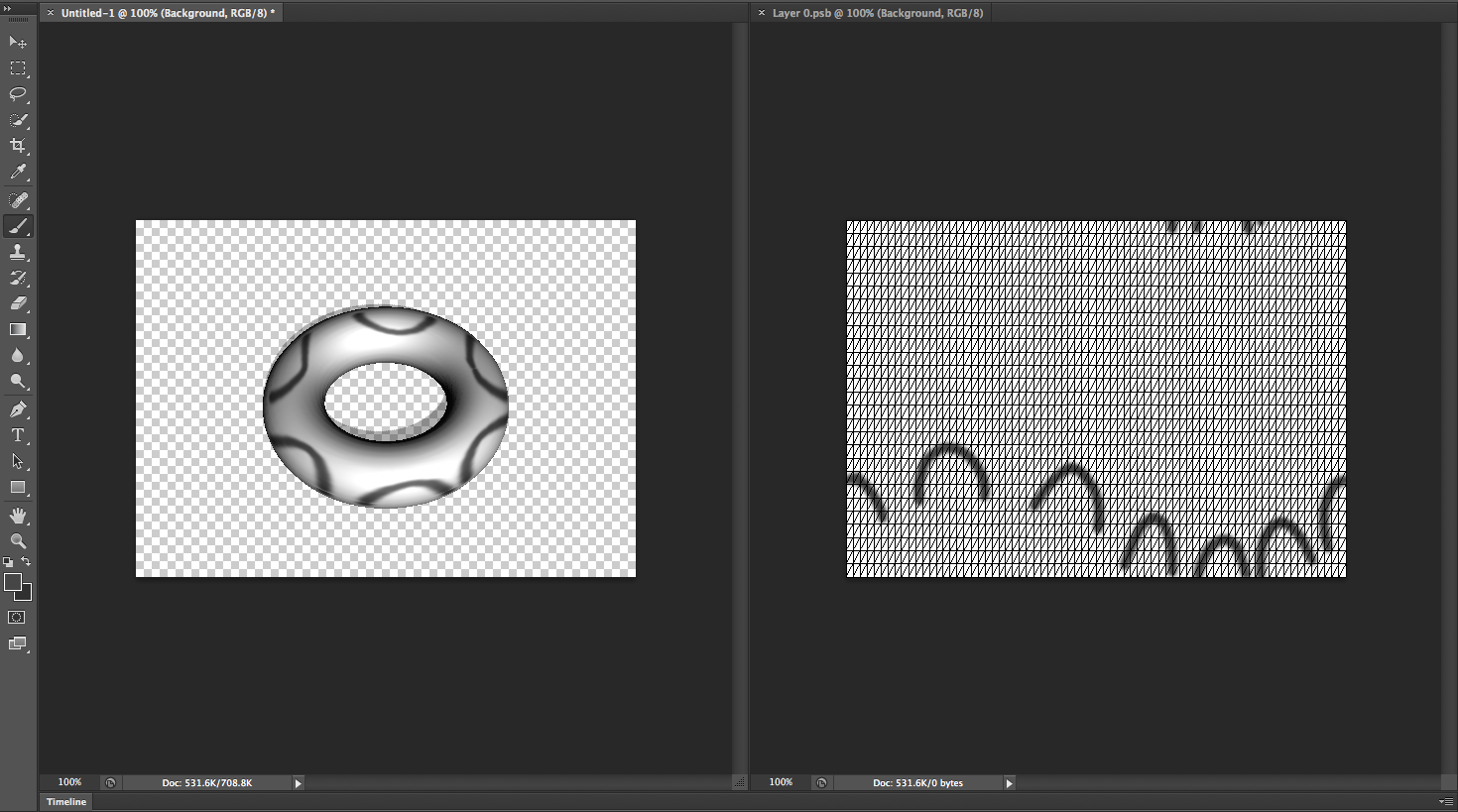
Some tips to paint 3D models
- If the model surface area is subconscious, you can temporarily cut away surface areas that are blocking your view. See Reveal surfaces to pigment on.
- If yous are painting on curved or irregular surfaces, you tin get visual feedback earlier you paint of which areas can best receive paint. See Identify paintable areas. You tin also set the paint fall-off angle, which controls the amount of pigment practical to angled surfaces. Run across Set the pigment falloff angle.
- While painting texture seams, a single castor postage stamp applies only to one side of the seam. Move the eye of the castor across the seam to pigment its other side.
- If you attempt to paint on a texture map type that the material doesn't comprise, Photoshop prompts you to create a map. For information on map types, see 3D Materials settings (Photoshop Extended).
Paint an object in the Alive 3D Painting style
- Open up the 3D model in the 3D model view.
- Open the texture document that yous want to paint. To practice so, double-click the proper name of the texture in the Layers panel.
- Select Window > Accommodate > Tile to view the 3D model view and the texture document adjacent.
- Using the Brush tool, paint the 3D model or the texture document. Your brush stokes reverberate automatically in the other view.
Switch to the Projection Painting style
- Create or open a 3D model.
- Select 3D > Use Projection Painting.
- Pigment your 3D model.
In the Main 3D certificate, Photoshop uses the Projection Painting method by default for painting operations.
Unwrap UVs of a 3D model
Photoshop provides an option to automatically unwrap UV maps for your 3D model.
- Open the 3D model.
- Select 3D > Generate UVs.
- The warning When using Generate UVs, all of the meshes' materials' textures will exist flattened is displayed. Click OK to continue.
- In the Generate UVs dialog box that appears, choose the following textile and unwrapping options:
Merge Materials
If multiple maps—for example, Diffuse and Crash-land maps—exist on a single mesh, combine them into one map.
Case: Combine ii different Diffuse maps into 1 Diffuse map.
If you accept multiple meshes, each of them will however have their own map. For case, if you have three separate meshes with iii Lengthened maps, you'll still accept 3 separate Diffuse maps for each mesh.
Preserve Appearance
On a best-endeavour basis, maintains the look of the 3D model and its textures when new UVs are generated. If you cull to not enable this selection, the electric current textures are not preserved.
UV Map Size
Select the required size for the generated UV maps (pixels x pixels). You have the option choose 128, 256, 512, 1024, 2048, or 4096.
Low Distortion
Keeps the texture blueprint more intact, but tin can create more seams on the model surface.
Fewer Seams
Minimizes the number of seams that appear on the model. This can produce more stretching or pinching of the texture, depending on the model.
- Click OK.
- You lot tin can view the generated UVs under the Diffuse section in the Layers panel.
After generating UVs for a Fuse model, the model moves from its original position. This is a expected behavior in most rigged models, as the rigged position is dissimilar from the position of the mesh. The model shifts to the mesh position because the rig is removed when generating UVs for that model.
To preview any of the generated UV maps, hold the cursor over the layer particular in the Layers panel. To open up the UV map in a separate window, doube-click that layer item.
Target a texture type for painting
You tin target eight unlike texture types for painting:
- With your 3D model open, select 3D > Paint On Target Texture.
- Choose the texture type that you want to paint.
In 3D models having multiple textures, but the texture that you open and start painting on is painted.

Paint in the unlit mode
You lot can choose to pigment your 3D objects in the unlit mode. This manner ignores any lighting in your scene and wraps raw texture information of the appropriate blazon around your 3D objects. Painting in the unlit mode lets you paint without shading and with greater colour accurateness.
Follow these steps:
- In the 3D panel, select Scene.
- In the Properties panel, select Surface.
- Select Unlit Texture from the Style pop-upward carte du jour.
Reveal surfaces to pigment on
For more complex models with interior or hidden areas, you lot tin can hibernate sections of the model for easier access to surfaces y'all want to paint. For example, to utilise paint to the dashboard of a auto model, you can temporarily cutting away the roof or windshield, then zoom within the machine to become an unobstructed view.
-
Select an expanse of the model that you want to cutting away, using a option tool such as the Lasso or Marquee tool.
-
Utilise any of the following 3D carte commands to reveal or hide areas of the model:
Hide Nearest Surface
hides only the commencement layer of model polygons within the 2D selection. To quickly peel away surface of the model, you lot can use this command repeatedly while keeping the choice area active.
When hiding surfaces, rotate the model if necessary to position surfaces so that they are perpendicular to your currentview.
Only Hide Enclosed Polygons
When selected, the Hide Nearest Surface command but affects polygons that are fully inside the selection. When unchecked, ithides any polygons touched by the selection.
Invert Visible Surfaces
Makes currently visible surfaces invisible, and invisible surfaces visible.
Reveal All Surfaces
Makes all hidden surfaces visible once again.
Set the paint falloff angle
When painting on a model, the paint falloff angle controls how much paint is applied to a surface as it curves away from the forrard-facing view. The falloff bending is calculated based on a "normal", or straight line projecting out from the part of the model surface that faces you. For case, in a spherical model such as a soccer ball, the falloff bending to the exact center of the ball as it faces y'all is 0 degrees. Equally the surface of the ball curves away, the falloff angle increases, up to 90 degrees at the edges of the ball.

A. Eye/camera angleB. Minimum angleC. Maximum angleD. Paint fade get-goE. Paint fade stop
-
Cull 3D > 3D Pigment Falloff.
-
Set the minimum and maximum angle settings.
-
The maximum paint falloff range is 0 - ninety degrees. At 0 degrees, pigment is only applied to the surface if information technology is facing directly forward, with no drop-off angle. At 90 degrees, paint tin can follow a curved surface such as a sphere to its visible edges. At a 45 caste setting, the painted expanse is express to the areas of the sphere that don't bend abroad at more than 45 degrees.
-
The Minimum falloff angle sets a range within which paint gradually fades as information technology approaches the maximum falloff bending. For case, if the maximum falloff bending is 45, and the minimum falloff is 30, paint opacity decreases from 100 to 0 percent betwixt 30 and 45 degrees of falloff.
-
Identify paintable areas
It may not exist articulate just from looking at a 3D model whether yous can successfully paint on certain areas. Because the model view may not provide a 1 to 1 correspondence with the 2nd texture itself, applying pigment direct to the model is unlike from directly painting on a 2d texture map. What appears to exist a small-scale brush on the model may in fact be much larger in relation to the texture, depending on the resolution of the texture, or how close y'all are to the model when applying paint.
Good paintable areas are areas where you can apply pigment or other adjustments to the model surface with the most consistent and predictable effect. In other areas, paint may be undersampled or oversampled due to your angle or distance from the model surface.
-
-
Choose 3D > Select Paintable Areas. A selection marquee highlights the best areas for painting on the model.
-
In Scene section
 of the 3D panel, choose Paint Mask from the Preset menu.
of the 3D panel, choose Paint Mask from the Preset menu.In Paint Mask mode, white shows areas skillful for painting, blue shows areas where pigment volition be undersampled, and red shows areas where pigment will be oversampled. (To paint on the model, you must change from the Pigment Mask render mode to a return way that supports painting, such every bit Solid.)
-
The areas selected past Select Paintable Areas, and the paintable areas shown in Paint Mask style, are partially adamant by the current Paint Falloff setting. A higher paint falloff setting increases the paintable area, a lower setting decreases the paintable area. Run into Gear up the paint falloff angle.
Source: https://helpx.adobe.com/photoshop/using/3d-painting-photoshop.html
0 Response to "draw texture on 3d object"
Enviar um comentário